
Once upon a time, the police knew the community and community members so well that if your interior lights were on later than usual, they would knock on your door and check to see if everything was well. Times have changed. Economic good fortune smiles, if not on everyone, then on more people than in the past, and glossy magazines offer readers images of well-stocked refrigerators and other scenes from a good life of consumer plenty. It is the era of Paris Hilton, Justin Bieber, and Beyonce. The American youth rebels are clad in leather and denim, wilding out of rap concerts. Replacing an old, destroyed World burdened with memory with a shimmy new and complacently forgetful one has become its own type of redemption. In the face of so much good fortune, maybe people feel less need for cosmic solace, less fear of cosmic retribution. No wonder we associate the post 911 years more with economic miracles than religious ones. However, some fear that various evils such as atomic weapons, genetic experimentation, chemical food additives, a massive overreliance on pharmaceuticals, and the fact that large portions of the Earth will soon become uninhabitable is an indication that people are becoming blind to godly powers. It is believed that people need to relearn it, to use spiritual powers to recover and maintain the divine order. Even Communist ideology is losing its influence on the minds of people in general, and of the young generation in particular, and it becomes apparent in a number of reports from Russia. #RandolphHarris 1 of 19

A very vivid description of this development was to be found in an article by Marvin L. Kalb, “Russian Youth Asks Some Questions.” The author reports from Moscow about a new questionnaire of the “Public Opinion Institute” of Komsomol Pravada, organ of the Communist youth organization. The paper found it necessary to ask questions like “Do you personally have a goal in life?”, “What is it?”, et cetera, not so much for the purpose of a statistical inquiry, but in order to combat the widespread phenomena of apathy and materialism, which are found in the young generation. This is the text of one letter, which is characteristic of others: “‘Are you satisfied with your generation?’ the questionnaire asked. ‘No!’ the nihilist answered. ‘Why’ the questionnaire asked. ‘I’m 19 years old,’ she explained, ‘ and I am filled with apathy and indifference to everything around me—so much so that grown-ups are surprised and wonder, “So young, and yet so bored; what will happen to her when she is 30?” However, this should not be surprising, for it is a simple fact: life is just not very interesting. And this view is not only my own, but all those people with whom I am friendly.’ ’Have you a goal in life?’ the questionnaire asked. ‘Earlier, when I still poorly understood life,’ she wrote, ‘I had a goal—to study. I finished high school; and now I am in an institute part time. But now all my pure dreams lead to only one thing money. Money is everything. Luxury, prosperity, love and happiness—if you have money, you can have all of these things, and more…I still do not know how I am going to get these things; but every girl dreams about a successful marriage with lots of money. Naturally, not everyone succeeds, for there are more people who want money than who have it…But I assure you I shall succeed. My conviction is based on the fact that I always do what I want; and what I want I normally get.’” #RandolphHarris 2 of 19

I do not mean to imply, of course, that his letter is representative of all the young generation in the Soviet Union. However, the survey and the publication of letters like this show how serious the leaders take the problem. We in the West, of course, should not be surprised. We are dealing with the same problems of juvenile delinquency and juvenile immortality, and for the same reasons. The materialism, prevalent in our system as well as in the Soviet Union, corrodes the sense of meaning of life in the young generation and leads to cynicism. Neither religion, humanist teaching, nor Marxist ideology is a sufficiently strong antidote—unless fundamental changes occur in the whole society. Just because ideology is not synonymous with lies, just because they—and we—are not aware of the reality behind the conscious ideology, we can not expect that they will—or could—tell us in an aside “we really do not mean what we say; all this is for public consumption, for keeping control over the minds of the people.” Maybe there is an occasional cynic who thinks this; but it is the very nature of ideology that it deceives not only others, but also those who use it. Hence the only way of recognizing what is real and what is ideology is through the analysis of actions and not in accepting words for facts. If I watch a father treating his boy harshly because he considers it his duty to teach him virtue, I shall not be so foolish as to ask the father for his motivations; instead I shall examine his whole personality, many other acts of his nonverbal manifestations, and I shall arrive at an evaluation of the weight of his conscious intention in comparison with his real motivation. #RandolphHarris 3 of 19

To return to the Soviet Union, what is its ideology? It is Marxism in its crudest form; the development of man is bound up with the development of productive forces. With the development of productive forces, techniques, modes of production, man develops his own faculties, but he also develops classes which become increasingly antagonistic to each other. The development of new productive forces is hampered by the older social organization and class structure. When this contradiction becomes sufficiently drastic the older social organization is changed to accommodate the full development of the productive forces. The evolution of mankind is a progressive one; both man and his domination of nature develop increasingly. Capitalism is the most highly developed system of economic and social organization, but the private ownership of the means of production throttles the full development of the productive forces and thus hinders the full satisfaction of the needs of all men. Socialism, the nationalization of the means of production plus planning, frees the economy from its shackles; it frees man, it abolishes classes and eventually the state. At present a strong state is still needed to defend socialism against attack from abroad, but the Soviet Union is already a classless, socialist society. Capitalism, still beset with its inherent contradictions, must one day adopt the socialist system, partly because of its incapacity to cope with its own contradictions, partly because the example of the socialist countries will be so compelling that all countries will want to emulate it. Eventually, then, the whole World will be socialist, and this will be the basis for peace and the full realization of man. #RandolphHarris 4 of 19

This, in short, the Soviet catechism. It contains a mixture of ideology and theory. There is one difficulty the Western observer must overcome. We are not surprised that medieval thinking was structured in the frame of reference of theology. History was seen in terms of God’s creation, man’s fall, Christ’s death and resurrection, and the final drama of the second coming of Christ. Controversies, and even purely political disputes, were expressed in terms of this central frame of refence. The eighteenth and nineteenth centuries had a secular political-philosophical frame of reference. Monarchy versus republic, liberty versus submission, environmental influence versus innate human traits, et cetera, were the battlefields. We in the West still think in a frame of reference that is partly religious, partly political-philosophical. The Russians, on the other hand, have adopted a new frame of reference, that of a socio-economic theory of history, which, according to them, is Marxism. The whole World is looked upon from this perspective, and argument and attacks are expressed in terms of it. For the Western observer for whom such theories are at best the business of a few professors, it is difficult to understand that the Russians constantly talk in terms of class struggle, conflicts with capitalism, victory of communism. The Westerner assumes that this talk must express an aggressive and active attempt to proselytize the World. It may be useful to remember that our religious ideology, in which, for instance, Christians believe that all men will eventually believe in the true God, et cetera, does not imply that we are all set to convert the pagans. It is simply that, considering our central frame of reference, we have to express our ideas in certain term; the Russians, have their frame of reference, do so in other. #RandolphHarris 5 of 19

Soviet thinking is evolutionary and sees as the central factor in human evolution the development of the productive forces, the transformation of one social system to the next higher one. This view is not ideological in the sense in which I have used the term, but is the way the Soviet leaders really look at history, following a crude form Mr. Marx’s historical theory. It is ideological only in the negative sense that the soviet leaders do not employ this theory to analyze their own system. (Such a Marxist analysis of the Soviet system would immediately show the fictitious character of Soviet ideology.) For most Western observers, however, the theory lends itself to serious misunderstanding. When the Communist catechism says, “Communism will be victorious all over the World,” or when Mr. Khrushchev said “We will bury you,” these statements should be understood in terms of their historical theory that the next stage of evolution will be that of communism, but that does not imply that the Soviet Union sees it as its task to bring about this change by force, subversion, et cetera. It is important to understand the ambiguity of the Marxian theory. It is a theory that claims that historical changes occur when the economic development permits and necessitates the change. This aspect of the theory is one that was the basis of socialist reformist thinking in Europe, as represented by Mr. Bernstein and others. These socialists believe in the “final victory” of socialism, but they postulated that the working class need not—and could not—push events. They held that capitalism had to go through all the necessary stages, and eventually, at some unspecified time in the future, it would transform itself into socialism. #RandolphHarris 6 of 19

Mr. Marx’s view was not as deterministic and passive as that. Although he too thought that socialism could be ushered in only when the economic conditions were ripe for it, he believed that at this point the working class and the socialist parties, who by then would be in the majority, would have to take an active part in defending the new system against all hostile attacks from the former ruling groups. Mr. Lenin’s position deviated from Mr. Marx’s in that he substituted the avant-garde for the working class, and that he had more faith in the efficacy of force, especially in a Russia which had not yet gone through its bourgeois revolution. The Marxist goal of the final victory of socialism was common both to the nonactivist reformists and to Mr. Lenin. The formula itself—“Final victory of communism”—is a historical prediction and perfectly applicable to an evolutionary, nonaggressive policy as represented by Mr. Khrushchev. In judging whether Mr. Khrushchev aimed at a “World revolution” it is useful to ask oneself what one means by “revolution.” Of course, the word can be used in many different meanings, the most general one being that of any kind of complete and violent change of an existing government. In this case, Mr. Hitler, Mr. Mussolini, and Mr. Franko were revolutionaries. However, if one uses the concept in a more specific sense, namely the overthrow of an existing, oppressive government by popular forces, then none of these three men could be called “revolutionaries.” In fact, this usage is generally accepted in the West. When we speak of the English, the French, the America revolutions, we refer to revolutions from below, and not from above; to the popular attack against authoritarian systems not to the seizure of power by an authoritarian system. #RandolphHarris 7 of 19

It was in this sense that Mr. Marx and Mr. Engels used the term revolution, and it was in this sense that Mr. Lenin believed he had started his revolution. He was convinced that the avant-grade expressed the will and the interests of the vast majority of the population, even though the system he created ceased to be the expression of popular will. However, the Communist “victories” in Poland, Hungary, et cetera, were not “revolutions” they were Russian military take-overs. Neither Stalin nor Mr. Khrushchev are revolutionaries; they are leaders of conservative, bureaucratic systems, the very existence of which is based on unquestioning respect for authority. It is naïve not to see the connection between the authoritarian-hierarchical character of a system and the fact that the leaders of such a system can not be “revolutionaries.” Neither Mr. Disraeli nor Mr. Bismarck were revolutionaries although they brought about considerable changes in Europe, and remarkable advantages for their respective countries; nor was Napoleon a revolutionary, even though he used the ideology of the French Revolution. However, even though Mr. Khrushchev is not a revolutionary, his belief in the superiority of communism is perfectly sincere. For him, and probably also for the average Russian, communism and socialism are not, as for Mr. Marx, a humanist system which transcends capitalism, but an economic system that produces more effectively, that avoids economic crises, unemployment, et cetera, and hence is more capable, in long run, of satisfying the needs of a mass and machine society. #RandolphHarris 8 of 19

This is exactly why the Russian Communists believe that peaceful competition between the two systems will eventually lead to the acceptance of the Communist system throughout the World. Their concepts, here as in so many other respects, are those of capitalism—competition in the sphere of economic efficiency. Yet we hesitate to accept Mr. Khruschev’s challenge to compete with his system, and we preferred to believe that he wants to conquer us by force of subversions. While the basis general aims of humanistic socialism are the same for all countries, each country must formulate its own specific aims in terms of its own traditional and present situation, and devise it own methods to achieve this aim. The mutual solidarity of socialist countries must exclude any attempt on the part of one country to impose its methods on another. In the same spirit, the writings of the fathers of socialist ideas must not be transformed into sacred scriptures which are used by some to wield authority over others; the spirit common to them, however, must remain alive in the hearts of socialists and guide their thinking. Humanistic socialism is the voluntary, logical outcome of the operation of human nature under rational conditions. It is the realization of democracy, which has its roots in the humanistic tradition of mankind, under the conditions of an industrial society. It is a social system which operates without force, neither physical force nor that of hypnoid suggestions by which humans are forced without being aware of it. It can be achieved only by appealing to man’s reason, and to his longing for a more human, meaningful, and rich life. #RandolphHarris 9 of 19

Humanistic socialism is based on faith in man’s ability to build a World which is truly human, in which the enrichment of life and the unfolding of the individual are the prime objects of society, while economics is reduced to its proper role as the means to humanly richer life. In discussing the goals of humanistic socialism we must differentiate between the final socialist goal of a society based on the free cooperation of its citizens and the reduction of centralized State activity to a minimum, and the intermediate socialist goals before this final aim is reached. The transition from the present centralized State to a completely decentralized form of society cannot be made without a transitory period in which a certain amount of central planning and State intervention will be indispensable. However, in order to avoid the dangers that central planning and State intervention may lead to, such as increased bureaucratization and weakening of individual integrity and initiative, it is necessary: a) that the State is brought under the efficient control of its citizens; b) that the social and political power of the big corporations is broken; c) that from the very beginning all forms of decentralized, voluntary associations in production, trade, and local social and cultural activities are promoted. While it is not possible today to make concrete detailed plans for the final socialist goals, it is possible to formulate in a tentative fashion the intermediate foals for the socialist society. However, even as far as these intermediate goals are concerned, it will take many years of study and experimentation to arrive at more definite and specific formulations, studies to which the best brains and hearts of the nation must be devoted. #RandolphHarris 10 of 19

Following the principle that social control and not legal ownership is the essential principle of socialism, its first goal is the transformation of all big enterprises in such a way that their administrators are appointed and fully controlled by all participants—workers, clerks, engineers—with the participation of trade union and consumer representatives. These groups constitute the highest authority for every big enterprise. They decide all basic questions of production, price, utilization of profits, et cetera. The stockholders continue to receive an appropriate compensation for the use of their capital, but have no right of control and administration. The autonomy of an enterprise is restricted by central planning to the extent to which it is necessary to make production serve it social ends. Small enterprises should work on a cooperative basis, and they are to be encouraged by taxation and other means. Inasmuch as they do not work on a cooperative basis, the participants must share in the profits and control the administration on an equal basis with the owner. Certain industries which are of basic importance for the whole of society, such as oil, banking, television, radio, medical drugs, and transportation, must be nationalized; but the administration of thee nationalized industries must follow the same principles of effective control by participants, unions and consumers. In all fields in which there is a social need but not an adequate existing production, society must finance enterprise which serve these needs. The individual must be protected from fear and the need to submit to anyone’s coercion. #RandolphHarris 11 of 19
In order to accomplish this aim, society must provide, free for everyone, the minimum necessities of material existence in food, housing, and clothing. Anyone who has higher aspirations for material comforts will have to work for them, but the minimal necessities of life being guaranteed, no person can have power over anyone of the basis of direct or indirect material coercion. Socialism does not do away with individual property for use. Neither does it require the complete leveling of income; income should be related to effort and skill. However, differences in income should not create such different forms of material life that the life experience of one cannot be shared by, and this remains alien to, another. The principle of political democracy must be implemented in terms of the twenty-first century reality. Considering our technical instrumentalities of communication and tabulation, it is possible to reintroduce the principle of the town meeting into contemporary mass society. The forms in which this can be accomplished need study and experimentation. They may consist of the formation of hundreds of thousands of small face-to-face groups (organized along the principle of place of work or place of residence) which would constitute a new type of Lower House, sharing decision-making with a centrally elected parliament. Decentralization must strive at putting important decisions into the hands of the inhabitants of small, local areas which are still subject to the fundamental principles which govern the life of the whole society. #RandolphHarris 12 of 19

However, whichever forms are to be found, the essential principle is that the democratic process is transformed into one in which well-informed and responsible citizen—not automatized mass-men, controlled by the methods of hypnoid mass suggestion—express their will. Not only in the sphere of political decisions, but with regard to all decisions and arrangements, the grip of the bureaucracy must be broken in order to restore freedom. Aside from decisions which filter down from above, activity in all sphere of life on the grass-roots level must be developed which can “filter up” from below to the top. Workers organized in unions, consumers organized in consumers’ organizations, citizens organized in the above-mentioned face-to-face political units, must be in constant interchange with central authorities. This interchange must be such that new measures, laws, and provisions can be suggested and, after voting, decided from the grass roots, and that all elected representatives are subject to continuous critical appraisal and, if necessary, recall. Origin of knowledge. –Over vast stretches of time, the intellect produced nothing but errors; some of them turned out to be useful and species-preserving: whoever hit upon or inherited them waged the battle for themselves and their offspring with better luck. Such erroneous articles of faith, which were further passed on and finally became almost the basic endowment of the human species, are, for example: that there are enduring things; that there are equal things; that there are things, materials, bodies; that a thing is what it appears to be; that our will is free; that what is good for me is also good in and for itself. #RandolphHarris 13 of 19

Only very late did the deniers and doubter of such propositions come on the scene—only very late did truth come on the scene as the weakest form of cognition. It seemed as if one could not live with it; our organism was geared to the opposite: all its higher functions, sense perception and every kind of sensation generally, worked with those fundamental errors, incorporated from archaic times. Moreover, even in the realm of knowledge those propositions became norms according to which one measured “true” and “untrue”—down to the mot remote regions of pure logic. Thus, the strength of knowledge lies not in its degree of truth but in its age, its being incorporated, its character as a condition of life. Where life and knowledge seemed to come into conflict, there was never any serios contest; denial and doubt were considered madness. Those exceptional thinkers, such as the Eleatics, who, in spite of everything, fixed and held fast to the opposite of the natural error, thought it possible also to live this opposite; they invented the sage as the man of immutability, impersonality, universality of intuition, as at once one and all, with a special capacity for that inverted knowledge; they were of the belief that their knowledge was also the principle of life. However, in order to assert all this, they had to deceive themselves about their own condition: they had to credit themselves with impersonality and duration without change to misconceive essence of knowledge, to deny the force of impulses in knowledge, and to conceive of reason in general as a wholly free, self-originating activity; they closed their eyes to the fact that they, too, had arrived at their propositions in opposition to what was considered valid, or from a desire for tranquility, or disinterestedness, or domination. #RandolphHarris 14 of 19

The more refined development of honesty and skepticism in the end rendered even these men impossible; their life and judgment, too, turned out to be parasitic on the age-old drives and fundamental errors of all sentient existence. That more refined honesty and skepticism arose where two antithetical propositions both seemed to apply to life, both being compatible with the fundamental errors, hence where it was possible to argue about greater and lesser degrees of utility for life; likewise, where new propositions showed themselves to be, if not especially useful to life, then at least not harmful either—expressions of an intellectual play impulse, innocent and happy like all play. Gradually the human brain filled itself with such judgments and convictions, and a ferment, a struggle, a craving for power emerged in this tangle. Not only utility and delight but every kind of impulse took part in the fight over “truths”; the intellectual fight became occupation, attraction, profession, duty, dignity; knowledge and striving for the true in the end took their place as a need among other needs. From then on, not only faith and conviction but also scrutiny, denial, mistrust, and contradiction became a power; all “evil” instincts were subordinated to knowledge, put in its service, and acquired the luster of the permissible, the honored, the useful, and finally the eye and the innocence of the good. Knowledge thus became part and parcel of life itself and as such an ever-increasing power—until finally knowledge and those age-old fundamental errors collided, both as life, both as power, both in the same man. The thinker: this is now the creature in whom the drive to truth and all those life-preserving errors wage their first battle, once the drive to truth has proved that it, too, is a life-preserving power. #RandolphHarris 15 of 19

Compared to the significance of this battle, all else is a matter of indifference: here, the ultimate question concerning the condition of life is posed, and here, the first attempt is made to answer the question with an experiment. To what extent can truth be incorporated?—that is the question, that is the experiment. Victory over the ultimate negative as a tempter, and all its temptations—whether direct or indirect—must be learned by the believer from personal experience. One must remember that not all “temptations” are recognizable as temptations, nor are they always visible—for half their power lies in their being hidden. A believer often thinks that one will be as conscious of the approach of temptations as one is of a person coming into the room. Hence the children of God are only fighting a small proportion of the ultimate negative’s workings: that is, only what they are conscious of as supernatural workings of evil. Because of their knowledge of the ultimate negative’s character and methods of working is limited and circumscribed, many true children of God only recognize “temptation” when the nature of the thing presented is visible evil, and accords with their limited knowledge of evil. So they do not recognize the temper and one’s temptations when they come under the guise of lawful and apparent “good.” When the ultimate negative and one’s emissaries come as angles of light clothe themselves in light, which, in their case, stands for evil. It is a “light” which is really darkness. They come in the guise of good—for darkness is opposed to light, ignorance is opposed to knowledge, falsehood is opposed to truth. #RandolphHarris 16 of 19

Darkness is a term we ordinarily apply to evil morality and moral darkness. Hence the believer may need to discern evil spirits in the realm of the supposed good. That which comes to them as “light” actually may be darkness. The apparent “good” may be really evil. And so the apparent “help” which the believer clings to may be really a hindrance. There needs to be a choice between good and evil made perpetually by every man. The Hebrew priests of old were specially called to discern and tech the people the difference between “the holy and the common,” “the unclean and the clean,” reports Ezekiel 44.23. Yet is the Church of Christ today able thus to discern what is good and what is evil? Does she not continually fall into the snare of calling good “evil,” and evil “good”? Because the thoughts of God’s people are so often governed by ignorance and limited knowledge, they can call the works of God “diabolic” and the works of the ultimate negative “divine.” For they are not taught the necessity of learning to discern the difference between “the unclean and the clean,” nor how to decide for themselves what is of God and what is of the ultimate negative—although they are unknowingly compelled to make a choice every moment of the day. Neither do all believers know that they have a choice between good and good, id est, between the lesser and the greater good—and the ultimate negative often entangles them here. The place of the church is in a purely vertical relationship to God, the distinction between the latent and manifest church is challenged, and, the Spirit which constitutes the churches is not the Spirit of Jesus. #RandolphHarris 17 of 19

The Gestalt of grace and the sacramental principle are vehicles for the holiness of the “is,” the actual presence of the divine which, in turn, provides the positive base for the prophetic demand for the holiness of the “ought.” Furthermore, the church portrays an image which it presents to the non-believer who is incapable of seeing its theological side. On the one hand, the latent church under the vivifying power of the Spiritual Presence is in preparation for the reception of the New Being in Jesus the Christ. However, the latent church is not simply an infant awaiting baptism; it is already a mature, adult member of the Spiritual Community, ad under the drive of the Spirit it voices criticism of the manifest church through non-sectarian, secular, or even anti-religious movements. Its protest appears as a cultural phenomenon, but the underlying inspiration is religious. On the other hand, the manifest church openly and consciously acknowledges the New Being in Jesus the Christ, and, united by the bonds of a common faith, it proclaims the Word of the Gospel and the sacraments of the New Law. However, these acts of religion must be expressed in relevant cultural form. The latent church joins the Spiritual Community by participation in the New Being, but it does not know Jesus crucified. The manifest church’s explicit acknowledgement of Jesus as the bearer of the New Being gains for it the symbol of the Cross, the Protestant principle of self-reformation which is the only antidote to demonization. Possession and non-possession of the Cross seems a clear-cut distinction. How can the secular World voice truly prophetic criticism unless it too has the Cross, the symbol of the struggle against the demonic, at least implicitly? #RandolphHarris 18 of 19

What does the explicit reception of the New Being in Jesus the Christ add to the manifest church? In the manifest church, one finds that the Christian Bible, the document of the reception of final revelation, the sacraments which deepen the experience of the New Being, and the corporate organization rallies and sustains Christians in their effort to live the Gospel. Here is certainly a concrete difference between the latent and manifest churches. However, what immediately springs to mind, the demonization and profanization into which these two churches inevitably fall makes one wonder if the transition from the latent to the manifest church is worth the price. It seems that most of the latter’s energy is expended in applying the Cross to correct its own ambiguities. The impression is that the latent church is dynamic, exciting, productive, and pregnant with hope, while the manifest church is tired, dull, weighed down with ambiguities, and moribund—despite the fact that it has received the New Being in Jesus the Christ. One is tempted to conclude almost blasphemously—because it has received the New Being in Jesus the Christ. All Americans are brothers, responsible for one another. I pledge allegiance to the flag of the United States of America, and to the republic for which it stands, one nation, under God, indivisible with liberty and justice for al. If there be among you a need may, do not harden your heart. The generous heart shall be enriched, and one that satisfies others hall be satisfied oneself. #RandolphHarris 19 of 19


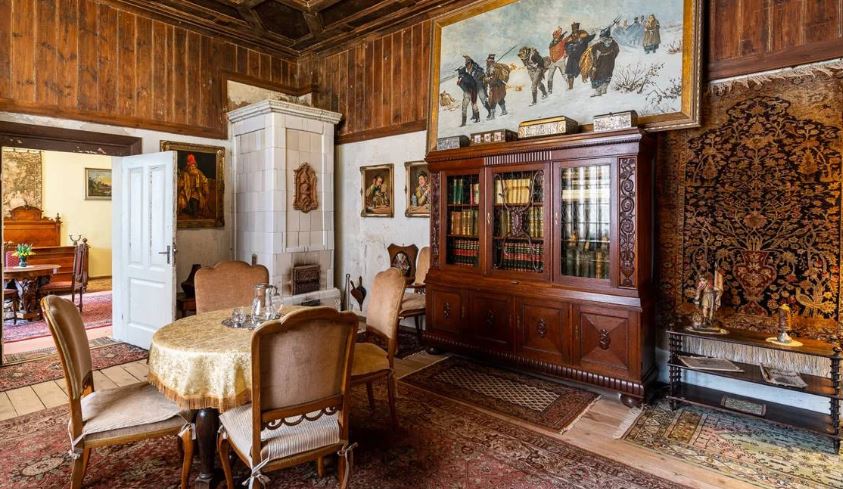
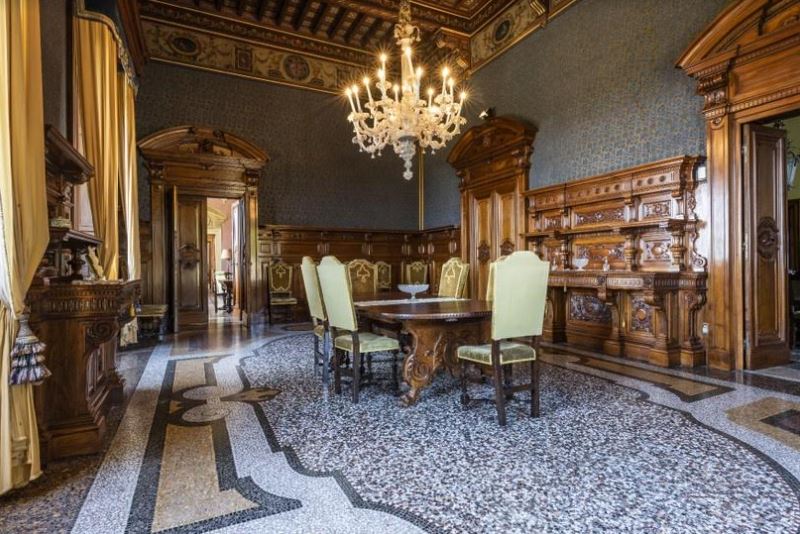
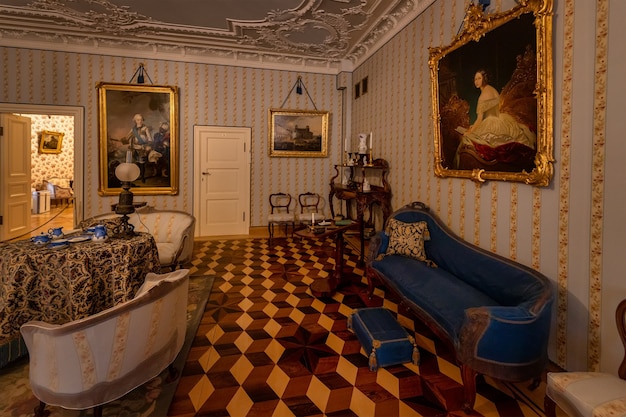
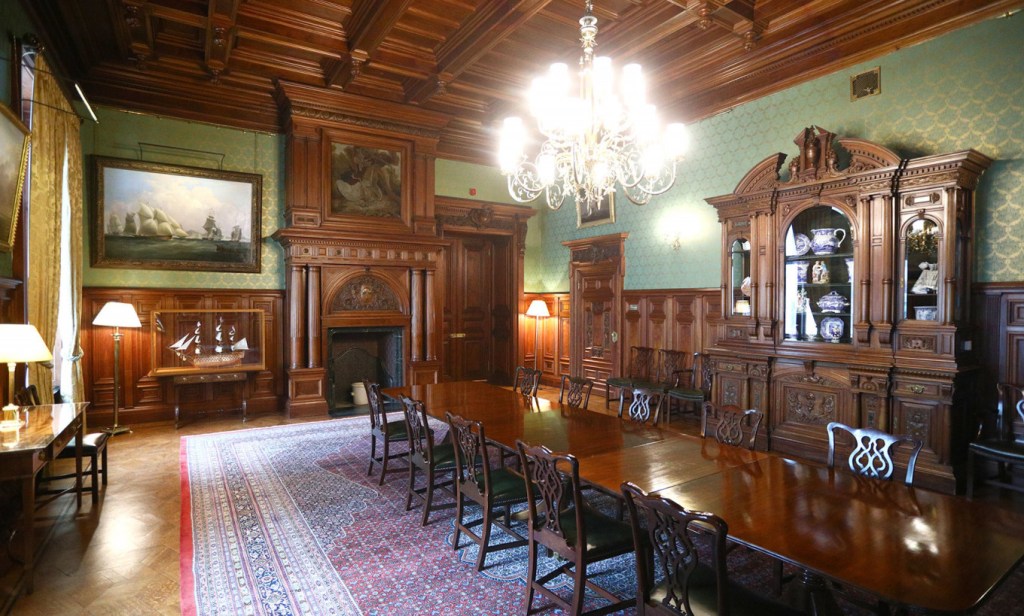
It is safe to say that the second most important room in the Victorian home was the dining room, where not only the family gathered, but where social interaction took place among family and visitors. In the family it should be observed as a rule to meet together at all meals of the day around one common table where the same rules of etiquette should be as rigidly observed as the table of a stranger.

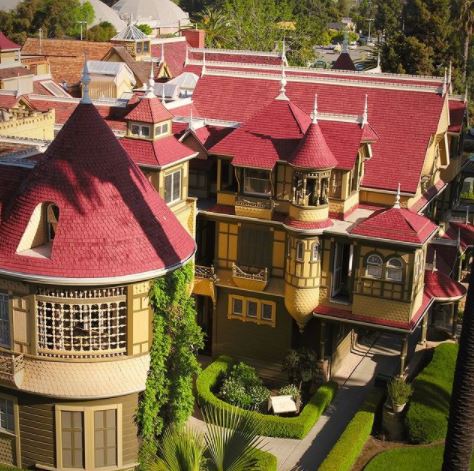
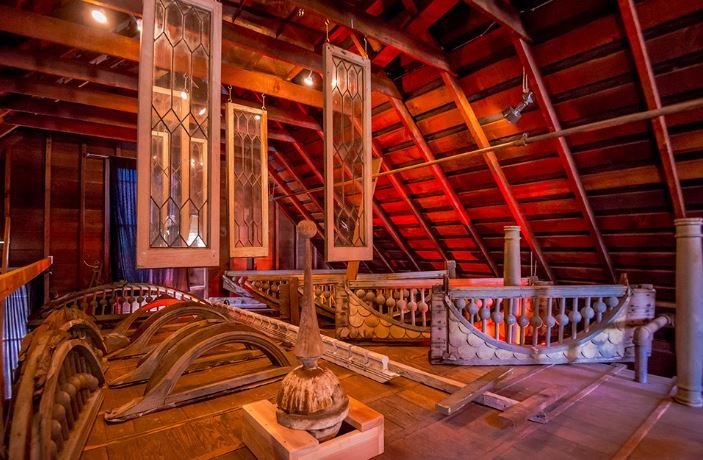
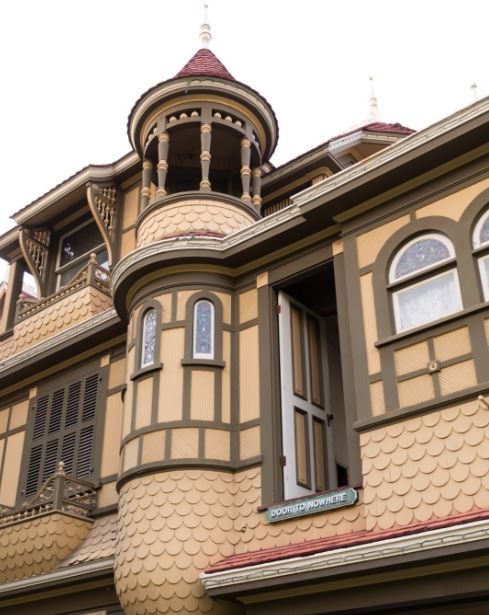
For further information about tours, including group tours, weddings, school events, birthday party packages, facility rentals, and special events please visit the website: https://winchestermysteryhouse.com/

Please visit the online giftshop, and purchase a gift for friends and relatives as well as a special memento of The Winchester Mystery House. A variety of souvenirs and gifts are available to purchase. https://shopwinchestermysteryhouse.com/




